Complexometric titration - titration curve calculation
Calculation of complexometric titration curve follows ideas outlined on the main titration curve calculation page. Before equivalence point amount of complex and excess titrated substance can be calculated from the reaction equation assuming that titrant was the limiting reagent. At the equivalence point we have just a solution of complex. After equivalence point situation reverses and concentrations of both complex and excess titrant can be calculated assuming titrated substance was the limiting reagent.
As it was already signalled in the complexometric titration equivalence point calculation section, when calculating titration curve we can be quite often forced to take solution pH into account.
What is concentration of Ca2+ in the 0.01 M CaCl2 solution titrated with 0.01 M EDTA if 24 mL of titrant were added to 25 mL of the sample. Assume pH of 12.5. Complex formation constant log Kf = 9.3, pKa1=2.07, pKa2=2.75, pKa3=6.24, pKa4=10.34.
First of all - do we have to worry about pH? pH is almost two units larger than pKa4. That means that over 99% of the EDTA will be in the form of conjugate base (EDTA4-) - and we can safely ignore its protonation.
We have 24+25=49 mL of the solution, that initially contained 25 mL×0.01 M=0.25 mmole of Ca2+. However, we have added 24 mL×0.01 M=0.24 mmole of EDTA, so assuming reaction went to the completion there is only 0.25-0.24=0.01 mmole of Ca2+ left. 0.01 mmole in 49 mL is 0.01/49=2.0×10-4 M.
Note: when calculating numbers of moles we have used very convenient shortcut, mixing molar concentration (expressed in moles/liter) with milliliters and millimoles of substance. Convenient as it is, it is a shortcut and should be used only when you understand when it can be used and why.
What is concentration of Cl- in 0.005 M solution of NaCl titrated with 0.01 M Hg(NO3)2 if 1 mL excess of titrant was added to 50 mL sample? log Kf = 13.2
This is an example of mercurymetric titration, rarely used these days because of mercury toxicity.
Reaction taking plac is that of chloride complex creation:
Hg2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) ↔ HgCl2(aq)
We started with 50 milliliters of 0.005 M solution. That means 0.05 L×0.005 M=2.5×10-4 moles of chlorides. To titrate this solution to the equivalence point we needed half of that amount of mercury - that is, 1.25×10-4 moles. This is 1.25×10-4/0.01 M=0.025 L of the mercury (II) nitrate solution, or 25 mL, for a total volume of 75 mL. Then we have added 1 mL of excess titrant, so the final volume is 76 mL.
Amount of complex is half that of initial amount of chlorides, that is 1.25×10-4. Thus concentration of the complex is
 1
11 mL of excess titrant contains 0.01 M×0.001 L=10-5 moles Hg2+. It didn't react, just got diluted to the final volume, so free mercury concentration is
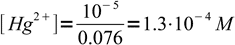 2
2To calculate concentration of chlorides we have to use complex formation constant:
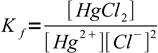 3
3we just solve it for chloride concentration and plug all already known numbers into derived formula:
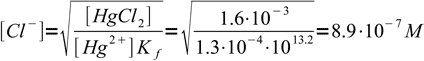 4
4



